Biliopancreatic limb length for Mini Gastric Bypass
Biliopancreatic limb length for Mini Gastric Bypass
The effect of biliopancreatic limb length on nutritional deficiencies, weight loss and comorbidity resolution after a Mini Gastric Bypass
The One Anastomosis, or Mini Gastric Bypass (OAGB) is an approved bariatric procedure to treat morbid obesity. However, there are concerns regarding the nutritional status of patients after this kind of surgery. This study aimed to find a consensus on the suitable biliopancreatic limb (BPL) length for the Mini Gastric Bypass, with a good balance between percentage excess weight loss, comorbidity resolution and nutritional deficiencies.
Set-up of the study
A retrospective analysis was conducted among 101 patients undergoing a Mini Gastric Bypass with either a BPL bypass of 150 cm (32 patients), 180 cm (49 patients) or 250 cm (20 patients). Patients were advised to take a high protein diet, protein supplements and vitamin supplements regularly. Weight, comorbidities and nutritional status were evaluated preoperatively and 1, 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively.
Weight loss and comorbidities after a Mini Gastric Bypass
The study found that the biliopancreatic limb length for Mini Gastric Bypass did not affect the amount of excess weight loss or comorbidity reduction. Comorbidities as diabetes type 2 and hypertension were greatly reduced independent of the BPL length. Similarly, the high percentages of excess weight loss did not differ significantly between the three groups. The only significant difference in total weight loss was found after 1 year, where the amount of weight loss was higher among patients with a longer BPL length.
Effect of biliopancreatic limb length on nutritional status
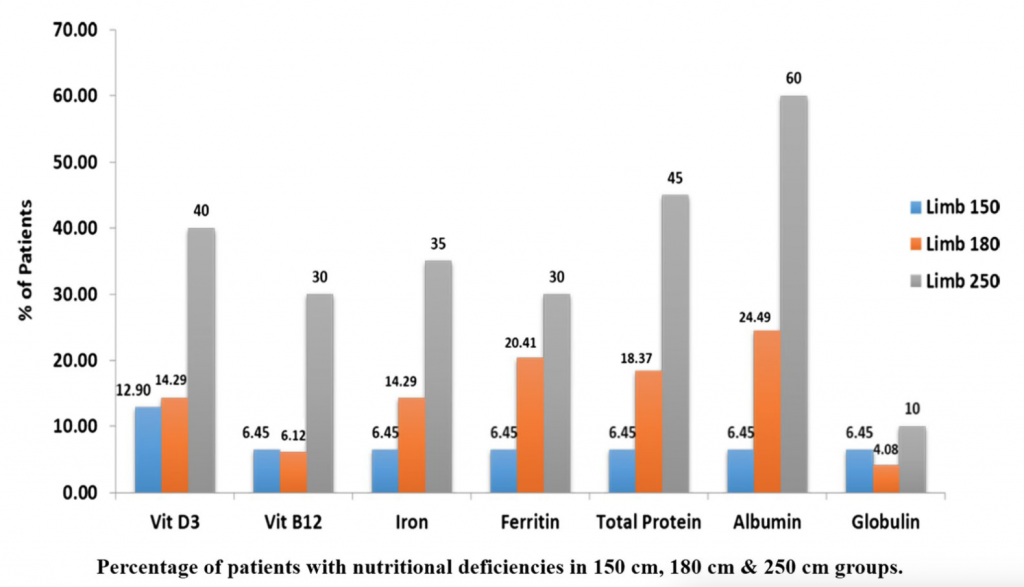
The longer the BPL bypass, the more deficiencies were observed. Deficiencies for vitamin D3 and B12 were significantly more frequent in patients in the 250 cm group (40% and 30%, respectively), while the deficiency prevalence was comparable between the 150 and 180 cm group. Furthermore, the deficiency prevalence for iron, ferritin, albumin and total protein increased significantly with a longer BPL length.
Figure 1: Percentage of patients with nutritional deficiencies in 150 cm, 180 cm, and 250 cm groups
Adequate biliopancreatic limb length for Mini Gastric Bypass
The study found that for most patients, 150 cm is an adequate BPL length with positive results on weight loss and comorbidity remission, without too much negative effect on the nutritional status. For super obese patients who require a greater total weight loss, a longer limb length of 180 cm or 250 cm may be used with utmost care for the nutritional status.
For more information about the article, get in touch with us by clicking the button below.
Reference:
Schijns, W., Boerboom, A., De Bruyn Kops, M., De Raaff, C., Van Wagensveld, B., Berends, F.J., Janssen, I.M.C., Van Laarhoven, C.J.H.M., De Boer, H., Aarts, E.O. (2020). A randomized controlled trial comparing oral and intravenous iron supplementation after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Clinical Nutrition, in press, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.010.
Link to full text: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0261561420301813





