Optimizing multivitamin supplementation for Sleeve Gastrectomy patients
Optimizing multivitamin supplementation for Sleeve Gastrectomy patients
Bariatric supplements
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (SG) is the most common bariatric procedure performed worldwide. After bariatric surgery, patients run the risk of developing nutritional deficiencies due to:
- Reduced dietary intake
- Decreased hydrochloric acid
- Decreased intrinsic factor
- Food intolerance
- Poor food choices
Preventing micronutrient deficiencies in bariatric patients requires lifelong supplementation with specialized multivitamins. In 2009, FitForMe introduced a multivitamin tailored for sleeve gastrectomy patients – WLS Optimum 1.0.
Multivitamin Optimization
In earlier studies, WLS Optimum 1.0 showed to be more effective in improving serum levels and reducing the risk of anemia compared to standard multivitamins. (Heusschen et al., 2019).
However, research findings revealed the need for further optimization resulting in an improved version of the specialized multivitamin in 2015 – WLS Optimum 2.0.
It’s worth noting that WLS Optimum 2.0 has since been further optimized to arrive at its current composition. Composition of WLS Optimum 2.2.
WLS Optimum 2.0 contained revised levels of the following micronutrients:
| Micronutrients | WLS Optimum 1.0* | WLS Optimum 2.0* |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 1.00mg | 0.80mg |
| Vitamin B1 | 2.00mg | 2.75mg |
| Folic Acid | 300.00μg | 500.00μg |
| Vitamin B12 | 10.00μg | 100.00μg |
| Iron | 21.00mg | 28.00mg |
| Copper | 1.00mg | 1.90mg |
| Zinc | 15.00mg | 28.00mg |
How did the improved version of WLS Optimum perform?
WLS Optimum 2.0 versus WLS Optimum 1.0
An open-label study (VITAAL II) was conducted to assess the short-term effectiveness of WLS Optimum 2.0 compared to WLS Optimum 1.0.
During a 12-month period, 76 patients were included to receive WLS Optimum 2.0. All participants underwent laboratory blood tests before surgery, 6 months after surgery, and 12 months after surgery.
In order to compare both versions of WLS Optimum, results from the VITAAL II study were coupled with results from a 2019 study on the efficacy of WLS Optimum 1.0 against standard multivitamin supplements (VITAAL I).
Serum blood levels
6 Months After Surgery — patients taking WLS Optimum 2.0 were found to have statistically significant higher mean serum levels for folic acid, zinc, and vitamin B12 compared to patients taking WLS Optimum 1.0.
12 Months After Surgery — patients taking WLS Optimum 2.0 were found to have statistically significant higher mean serum levels for vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 and lower levels of MCV compared to patients taking WLS Optimum 1.0.
Over a year after surgery, the mean increase in serum levels of phosphate, vitamin B6, and zinc was higher for patients taking WLS Optimum 2.0 compared to the group taking WLS Optimum 1.0.
12-month change in serum levels
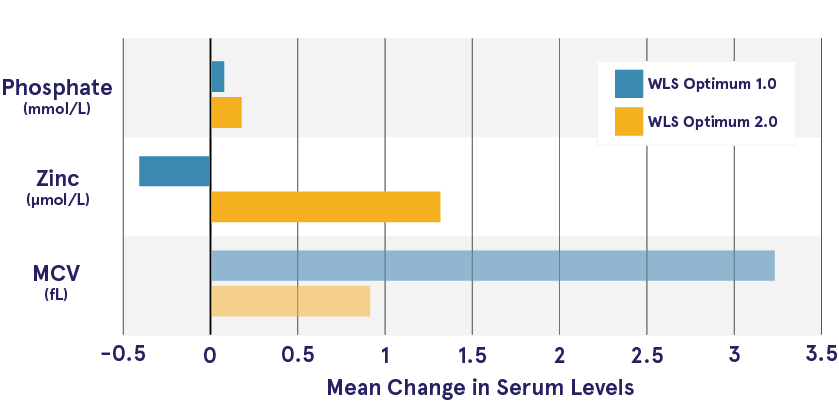
On the other hand, serum values for MCV and vitamin D increased more in the WLS Optimum 1.0 group. The higher increase in vitamin D for WLS Optimum 1.0 patients is due to lower baseline levels for this group. Serum levels and deficiencies were similar for both groups at 6 months and 12 months after surgery.
12-month change in serum levels
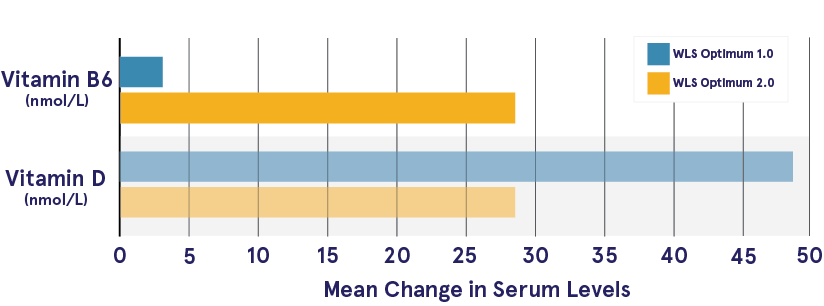
Although most of these results can be interpreted as favorable for bariatric patients taking WLS Optimum 2.0, the higher increase in vitamin B6 was noted to be above recommended levels. The latest version of WLS Optimum has been revised to reduce the risk of vitamin B6 hypervitaminosis.
No significant differences were found for other micronutrients between the two groups.
Nutritional deficiencies
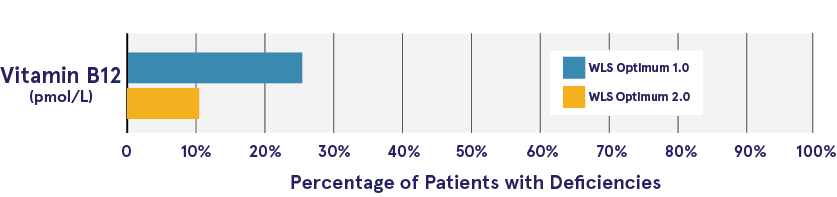
Differences in micronutrient deficiencies between the two groups were found for vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 deficiencies were more frequent in the WLS Optimum 1.0 group at 12 months post sleeve gastrectomy.
Deficiencies 12 months after surgery
Final thoughts
Heusschen et al. concluded that specialized multivitamin supplements are effective in preventing micronutrient deficiencies in sleeve gastrectomy patients.
WLS Optimum 2.0 proved to be a successful improvement over its predecessor. Researchers recommended lowering the level of vitamin B6 to decrease the risk of toxicity, a change that is already implemented in the current version of WLS Optimum.
Based on preliminary findings of this study and the latest scientific insights, FitForMe changed the dosage of vitamin D in 2017. In 2019, the composition of WLS Optimum was optimized again for vitamin B2, vitamin B6, and vitamin E.
Would you like to learn more about this research study?
Simply contact us using the button below:
Source: Heusschen, L., Berendsen, A. A., Cooiman, M. I., Deden, L. N., Hazebroek, E. J., & Aarts, E. O. (2021). Optimizing Multivitamin Supplementation for Sleeve Gastrectomy Patients. Obesity surgery, 1-9.





